This short paper, which was created within the Analysis and Modeling seminar, applies landscape metrics on potential habitats of the Eurasian Lynx in Germany. Landscape metrics are used to quantify the structure, composition and configuration of landscapes. Learn more about the methods and its use cases in the following paragraphs.
Abstract
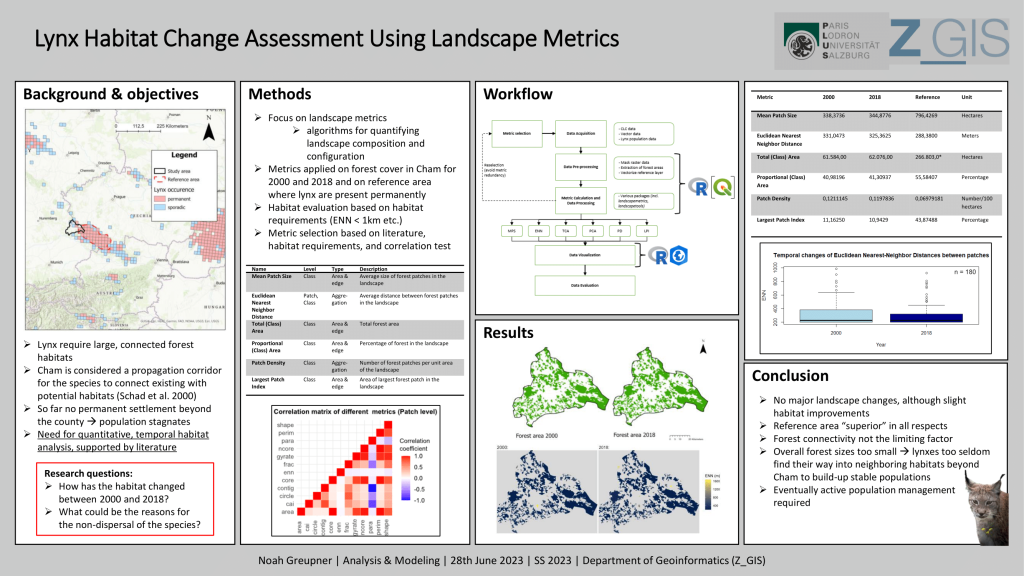
The Eurasian Lynx (Lynx lynx) is a European predator cat which is currently reintroduced in many European regions. The county of Cham in South East Bavaria is considered a propagation corridor for the species, potentially connecting the Bohemian-Bavarian-Austrian Lynx Population with possible habitats further north. This short paper uses landscape metrics to assess the habitat changes experienced by the lynx in Cham between 2000 and 2018 and evaluates the results by linking them to the species’ requirements. Specifically, six different metrics are used to measure habitat changes between the two years. These metrics are (1) Mean Patch Size, (2) Total Class Area, (3) Proportional Class Area (4) Patch Density, (5) Largest Patch Index and (6) Euclidean Nearest Neighbor Distance. By doing so, this paper contributes to understanding the impact of habitat changes on lynx populations and, thus, helps to develop effective conservation and propagation strategies in the region.
Poster